Introducing the keto diet into everyday life requires not only changing eating habits but also careful monitoring of the body’s condition.
One of the key aspects of successfully adhering to the keto diet is regularly measuring ketone levels.
In this material, we will examine various methods for measuring ketones, provide recommendations for their use, and discuss how to correctly interpret the obtained data to achieve optimal results on the keto diet.
What are ketones and why measure them
Ketones are organic compounds produced in the liver during fat breakdown.
Under normal conditions, the body uses glucose as its primary energy source. However, during carbohydrate deficiency, such as when following a keto diet, the body switches to using fats, producing ketones, which serve as an alternative energy source.
Regular monitoring of ketone levels allows not only tracking progress on the keto diet but also timely identifying possible deviations that may require adjustments in diet or lifestyle.
A high level of ketones indicates that the body is in a state of ketosis, which means successful fat burning for energy.
At the same time, excessively high ketone levels can lead to a condition known as ketoacidosis. This condition requires medical intervention.
Regular measurement of ketones allows timely dietary adjustments and maintaining a safe level of ketones in the blood. This is especially important for people with type 1 diabetes, as they have a significantly higher risk of developing ketoacidosis.
Methods for measuring ketones
There are several primary methods for measuring ketone levels in the body, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Below are the most popular tools for monitoring ketones.
Ketone strips for urine analysis
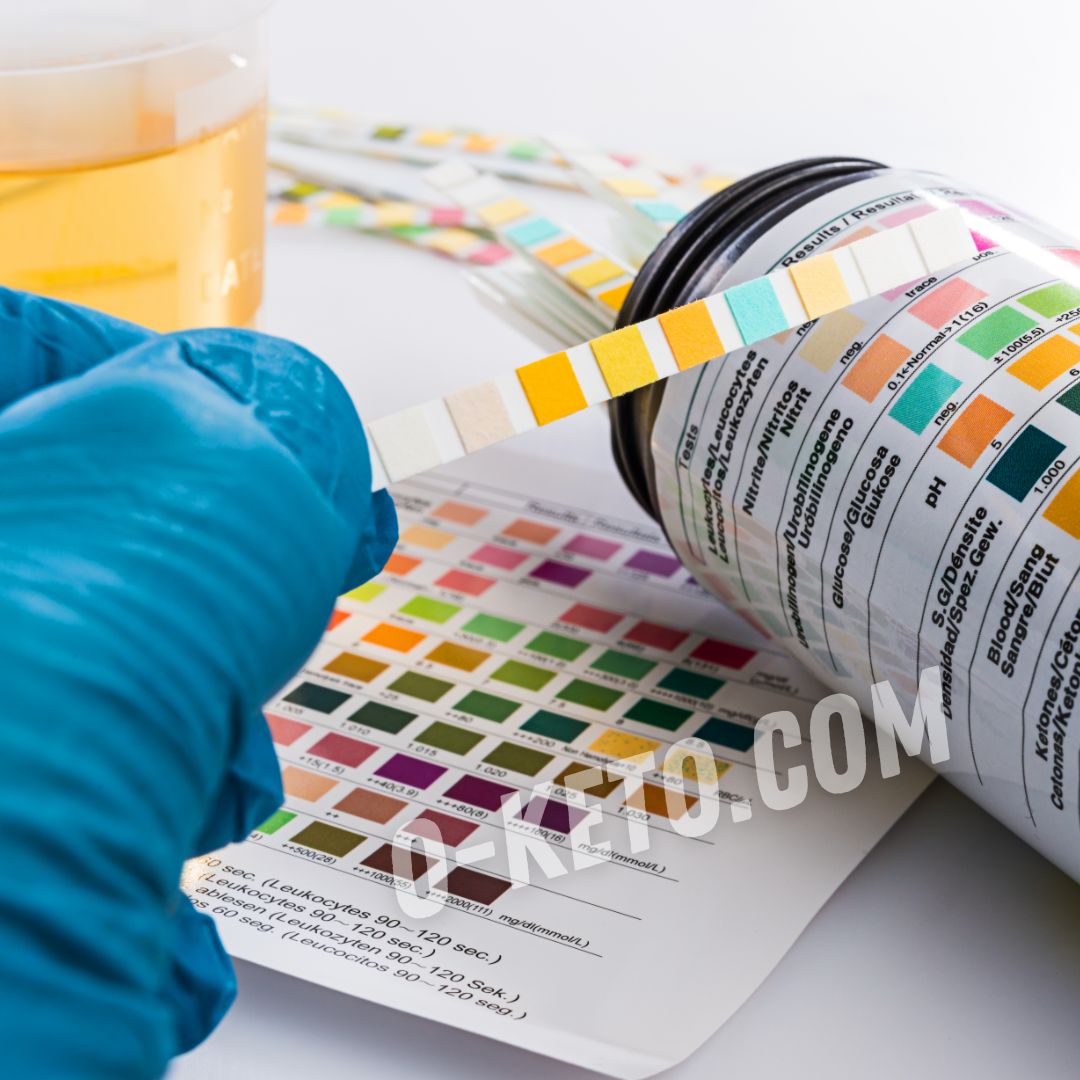
Ketone strips are the most accessible and straightforward way to measure ketones.
They work by dipping the strip into a urine sample, after which a color change occurs, indicating the level of ketones.
This method is particularly popular among beginners as it is inexpensive and requires no special skills.
Ketone glucometers
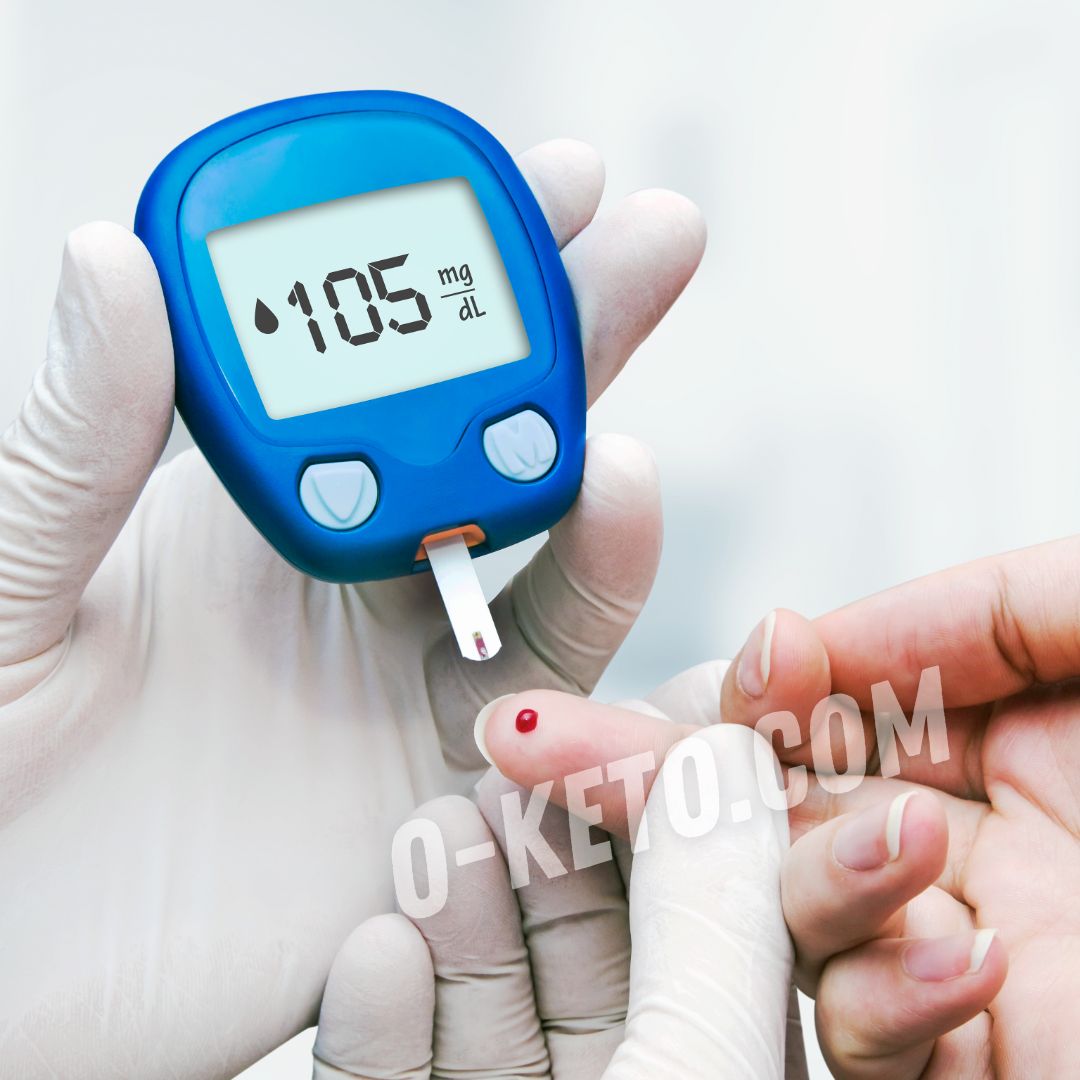
Ketone glucometers measure ketones in the blood, providing more accurate results compared to urine strips.
A small amount of blood is required for measurement, which is applied to the test strip. Results are usually displayed on the device’s screen within a few seconds.
This method is suitable for those who want to obtain the most reliable data.
Breath ketone analyzers
Breath analyzers measure acetone levels in the exhaled air.
These devices are convenient to use and do not require skin puncturing.
Measurement results may be less accurate than those from glucometers, but breath analyzers are especially convenient for regular monitoring throughout the day.
Methods for determining ketones without equipment
For those who prefer to do without special tools, there are “folk” methods for determining ketone levels.
Although these methods cannot provide precise data, they can serve as indicators of ketosis state.
Breath odor. One sign of ketosis is a specific fruity odor from the mouth reminiscent of acetone.
This is due to the release of volatile ketone bodies through breathing.
Changes in taste sensations. Some people report a metallic or sweet taste in the mouth, which may indicate an increased amount of ketones.
Energy level. Upon entering ketosis, many people experience an increase in energy levels and improved concentration.
Decreased appetite. Ketosis is often accompanied by a reduction in hunger, which is related to the effect of ketone bodies on appetite-regulating signals.
It is important to remember that these methods are subjective and may vary depending on individual body characteristics.
For more accurate data, it is recommended to use specialized ketone measurement tools.
How to properly use blood ketone tests
To correctly measure ketones in the blood, it is essential to follow specific steps to obtain accurate and reliable results.
Below are the key steps:
- Preparation: Make sure you have all the necessary materials: a glucometer for measuring ketones, test strips, lancets, and alcohol wipes. Wash your hands with warm water and soap, and dry them thoroughly before starting the procedure.
- Setting up the device: Insert the test strip into the glucometer, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the glucometer is ready for use and displays the appropriate symbol or code on the screen.
- Blood sample: Using a lancet, prick the side of your finger. Gently massage the finger to obtain a drop of blood. Do not squeeze the finger too hard, as this may affect measurement accuracy.
- Measurement: Bring the test strip to the drop of blood so that it absorbs into the specified area on the strip. The glucometer will automatically begin analyzing the sample and will display the ketone level in the blood on the screen within a few seconds.
- Recording results: Record the obtained data in a diary or app for tracking ketones. This will help you monitor your levels and adjust your diet if necessary.
Measuring ketones in urine: pros and cons
Measuring ketones in urine is a popular and accessible method for people following the keto diet. This method involves using test strips that change color in the presence of ketones. However, like any measurement method, it has its pros and cons.
Pros:
- Accessibility: Urine ketone test strips can be easily purchased at a pharmacy without a prescription, and they are relatively inexpensive.
- Ease of use: The testing procedure does not require special training or equipment. Simply dip the strip into urine and compare the color with the control chart.
- Quick results: Results can be obtained within a few minutes, allowing for a quick assessment of the state of ketosis.
Cons:
- Inaccuracy: Ketone levels in urine can vary depending on hydration, time of day, and other factors. This can lead to inaccurate results.
- Limited information: Test strips only indicate the presence of ketones but do not provide their quantitative content in the blood, which may be important for more precise monitoring.
- Body adaptation: With prolonged adherence to the keto diet, the body may start to utilize ketones efficiently, and their levels in urine may decrease even if you are in a state of ketosis.
Tips for interpreting results and actions in case of deviations
When measuring ketone levels, it is crucial to interpret the results correctly.
If the ketone level in the blood is in the range of 0.5-3.0 mmol/L, this indicates a state of mild or moderate ketosis, which is normal for the keto diet.
If the ketone level exceeds 3.0 mmol/L, this may be a sign of ketosis but could also indicate potential problems, such as ketoacidosis, especially in people with diabetes.
If you notice deviations in your ketone levels, follow these recommendations:
Elevated ketone levels. If the ketone level exceeds 3.0 mmol/L, consult a doctor immediately. This may be a sign of ketoacidosis, which requires medical intervention.
Low ketone levels. If the ketone level is below 0.5 mmol/L, this may indicate insufficient adherence to the keto diet.
Reassess your diet and ensure you are consuming enough fats and limiting carbohydrates.











