Flavonoids are a group of natural compounds belonging to the polyphenol class and play an important role in the plant world.
In recent years, the scientific community has increasingly focused on flavonoids due to their potential health benefits for humans. These compounds possess antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-carcinogenic properties, making them an integral part of a balanced diet. They may reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases and certain forms of cancer.
Flavonoids are found in a wide variety of plants and serve as pigments that give color to flowers and fruits. They also play an important role in protecting plants from ultraviolet radiation and pathogens.
In the human body, these nutrients contribute to strengthening blood vessels, regulating cellular activity, and may even reduce the risk of developing certain diseases.
The Role of Flavonoids in the Human Body
Flavonoids perform important functions in the human body. They are known for their antioxidant properties, which help combat free radicals and prevent oxidative stress (which can lead to various chronic diseases).
Combatting Inflammation. Studies show that certain flavonoids can reduce levels of inflammatory markers in the body.
Heart Health. Research indicates that regular consumption of flavonoid-rich foods may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Cognitive Functions. Some studies link flavonoid consumption to improved memory and overall cognitive activity.
Antitumor Action. Research shows that some flavonoids may inhibit the growth of cancer cells (in laboratory conditions).
Vitamin Absorption. They help the body absorb vitamin C and other essential nutrients.
Increasing Serotonin Levels in the Brain. This may help improve mood and reduce depressive states.
Blood Sugar Levels. Some studies suggest that flavonoids may improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose levels.
Allergy Relief. Some research indicates that flavonoids may reduce allergic reactions by blocking histamine release.
Skin Health. They may protect the skin from UV damage and improve its overall condition.
Digestion. They can support gut flora health and aid in normalizing digestive processes.
Daily Requirement and Sources of Flavonoids
The daily requirement for flavonoids is not precisely established, as they are not essential nutrients, and there are no specific recommendations for their intake.
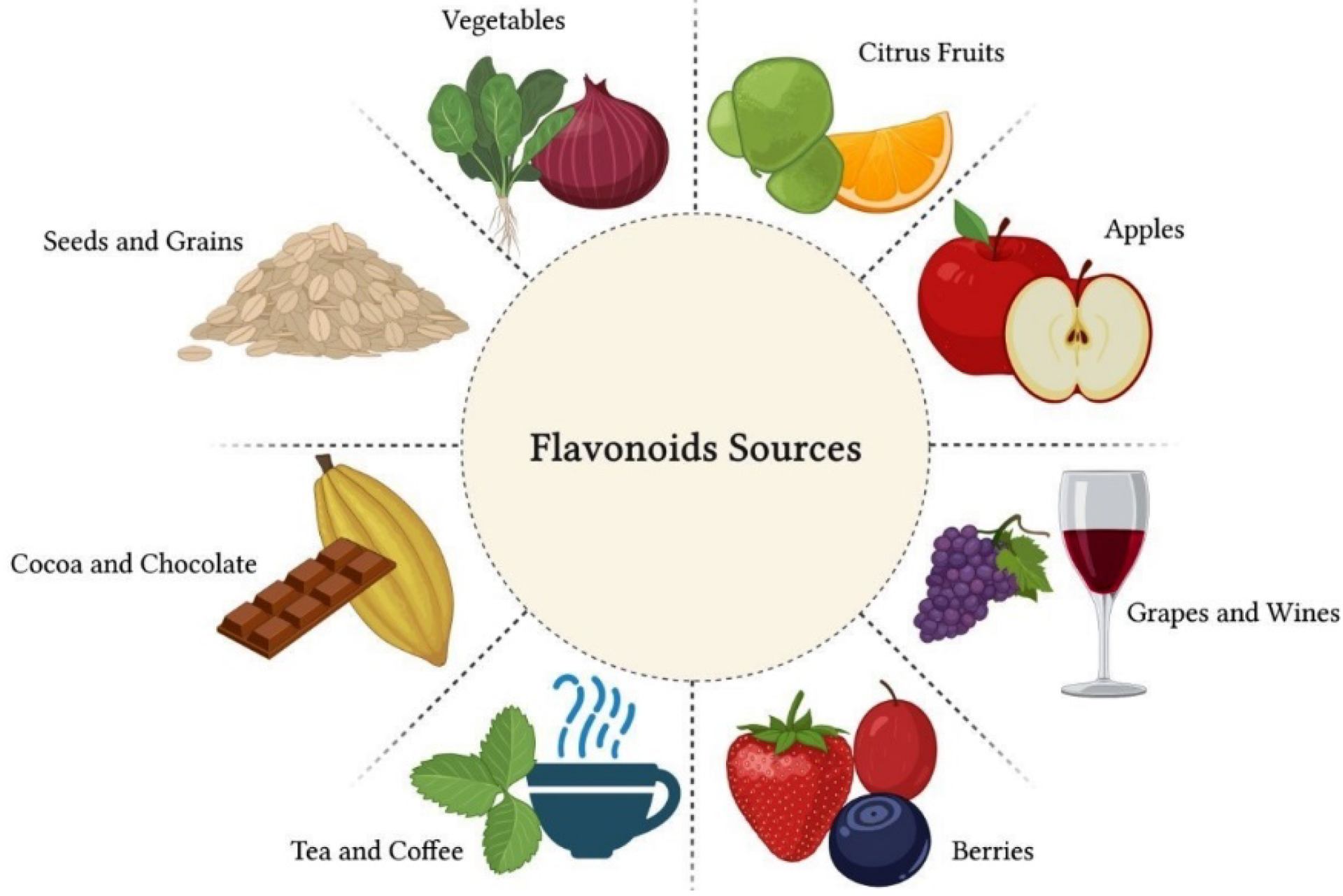
Flavonoids are found in a wide range of foods, making them accessible for inclusion in various diets.
Foods high in flavonoids include:
- Fruits and Berries: apples, grapes, pears, berries, and citrus fruits.
- Vegetables: onions, parsley, spinach, and broccoli.
- Beverages: tea, especially green and black tea, and red wine.
- Chocolate: dark chocolate with high cocoa content.
On a keto diet, it is important to choose foods that are not only rich in flavonoids but also low in carbohydrates. Such foods include:
- Berries: blueberries, blackberries, and raspberries in moderate amounts.
- Vegetables: spinach, avocado, and other leafy greens.
- Beverages: green and black tea without added sugar.
- Chocolate: dark chocolate with over 85% cocoa content and minimal sugar.
Studies show that some types of mushrooms may also contain significant amounts of flavonoids.
Incorporating these foods into the daily diet can help increase flavonoid intake and utilize their potential health benefits.
Flavonoid Deficiency and Related Issues
A deficiency of flavonoids in the diet may lead to a decline in the body’s antioxidant protection, increasing the risk of various inflammatory diseases and some forms of cancer.
Moreover, a lack of these compounds can negatively affect cardiovascular health, increasing the likelihood of hypertension and ischemic heart disease.
Possible Risks of Excessive Flavonoids and Their Prevention
Although flavonoids are important dietary components, excessive intake can also lead to undesirable effects. This is particularly true for flavonoids consumed in the form of concentrated dietary supplements. High doses may affect the absorption and metabolism of various substances, including medications, potentially leading to interactions with drugs.
To prevent excess flavonoids, it is recommended to consume them in their natural form, through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and other plant products.
Interesting Facts About Flavonoids
Flavonoids get their name from the Latin word “flavus.” This word translates to “yellow,” which relates to the bright colors of many plants that contain these compounds.
There are over 6000 known flavonoids. These compounds are divided into various subgroups, such as flavonols, flavones, isoflavones, and anthocyanins, each with its unique properties.
Anthocyanins, a subgroup of flavonoids, are responsible for the red and blue colors of fruits and vegetables. Examples include blueberries, raspberries, and red cabbage.
Flavonoids are often used as natural colorants. They can provide bright colors to food products and cosmetics.


















